SDS Optic S.A. develops the first in the world technology for robotic biopsy supported by 3D visualization with the possibility of molecular analysis
December 18, 2025
SDS Optic conducted an experiment at the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine of the University of Life Sciences in Lublin, using the inPROBE® microsensor supported by 3D visualization provided by CarnaLife Holo technology and precise device guidance from an Accrea robotic arm. The collaborating parties combined their technologies to test compatibility and to assess the feasibility of developing a robotic tool for highly precise tissue biopsy and molecular analysis, both in vivo and in vitro.
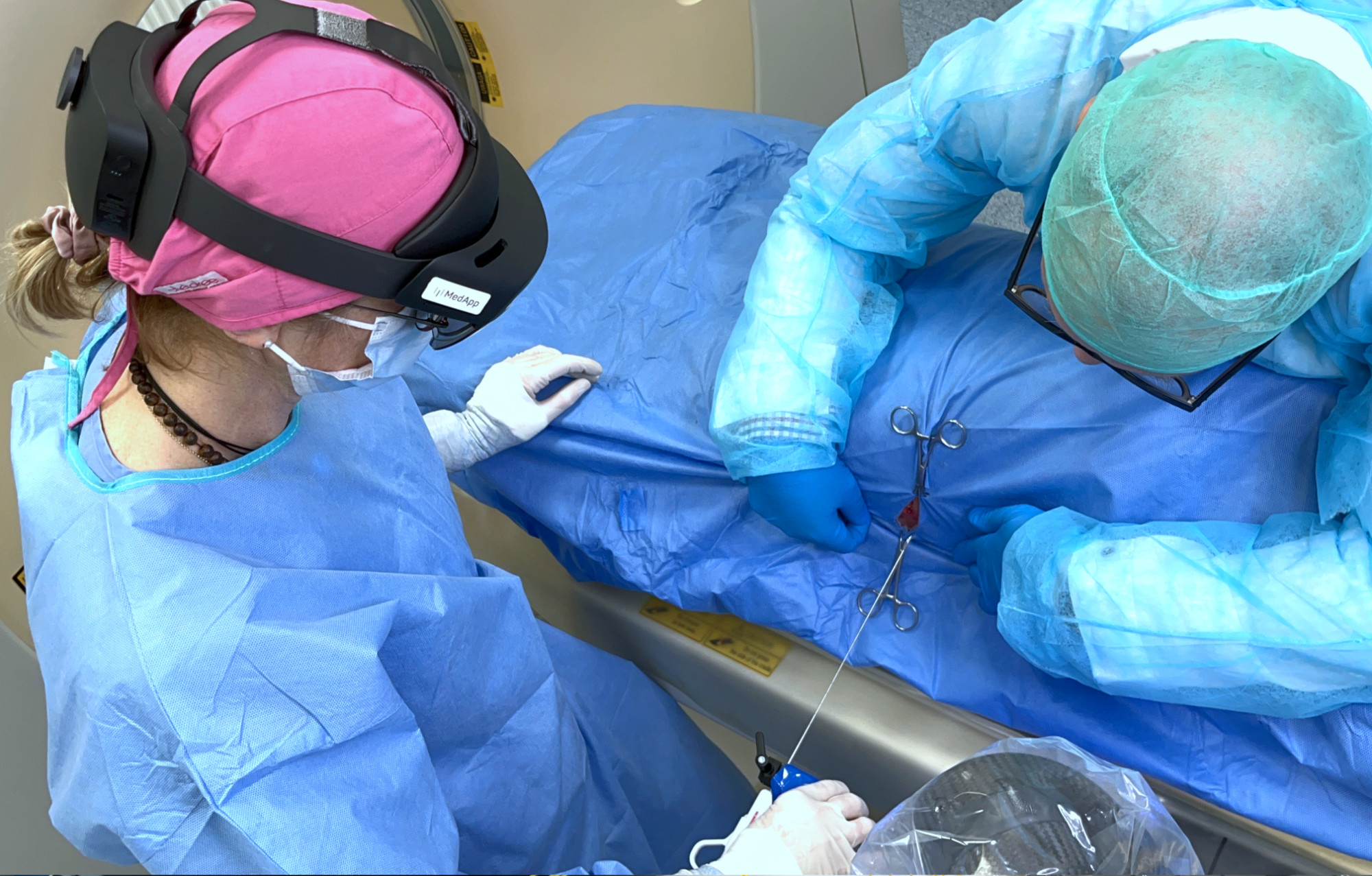
- SDS Optic S.A. was responsible for organizing and conducting the experiment, as well as for providing and configuring the inPROBE® microsensor based on photonic biosensors for real-time molecular biomarker detection.
- ACCREA MEDICAL ROBOTICS Sp. z o.o. introduced its own robotic arm for precise guidance of biopsy devices into the experiment, which during the test procedure also helped to precisely guide the inPROBE® microsensor to the selected location.
- MedApp S.A. provided the CarnaLife Holo software, enabling 3D visualization of diagnostic data in the form of extended reality projections to support and precisely conduct the experiment.
The study was conducted on a live animal model, by Beata Nowicka, PhD (Veterinary Sciences) with the assistance of a radiologist from the Department and Clinic of Veterinary Surgery and a team of specialists from the companies involved in the experiment.

- The experiment ran exceptionally well. I conducted the biopsy manually, as well as using the tested technologies. In my opinion, the assistance of the robotic arm and 3D visualization significantly improved the process, allowing for precise reach to the selected location in the object being studied. The support technology for biopsies, or, more broadly, surgical procedures combined with the possibility of additional molecular measurement, if supported by sufficient scientific evidence, could positively influence diagnostic procedures worldwide. The tested technologies could be used in human and veterinary medicine, including horses. - says Beata Nowicka, PhD (Veterinary Sciences) from the University of Life Sciences in Lublin.
Details of the experiment and results
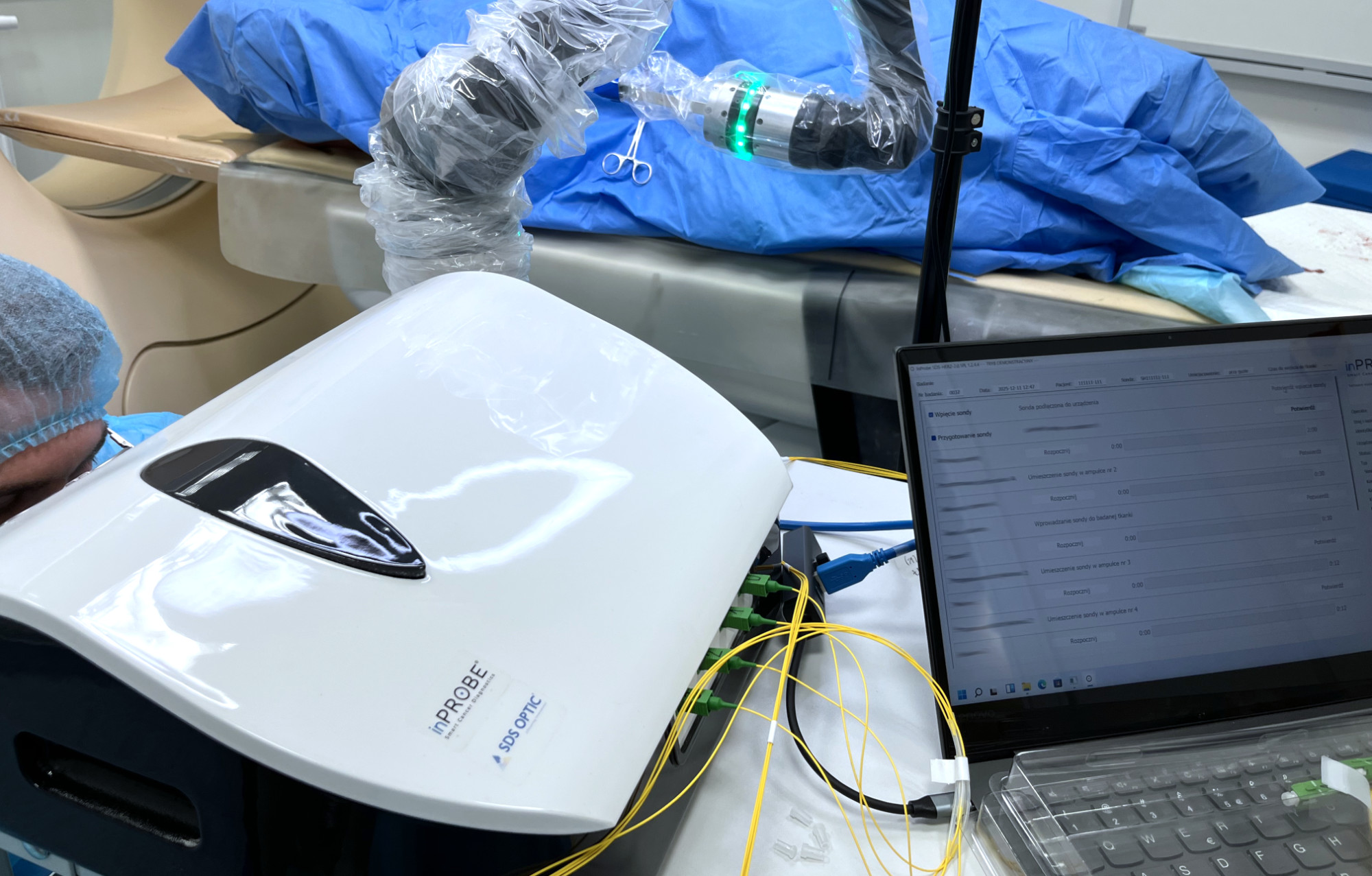
The object to be studied was introduced into the tomography and scanned layer by layer. Images, using special software MedApp, were converted into 3D graphics of selected areas. The doctor, using a robotic arm equipped with a specially adapted biopsy needle, performed the biopsy. The biopsy was performed under the control of vision through special glasses, allowing 3D visualization of the selected organ. After introducing the biopsy needle into the appropriate location (indicated by interactive markers) the doctor placed the inPROBE® microsensor in the target location, performing the corresponding molecular measurements.

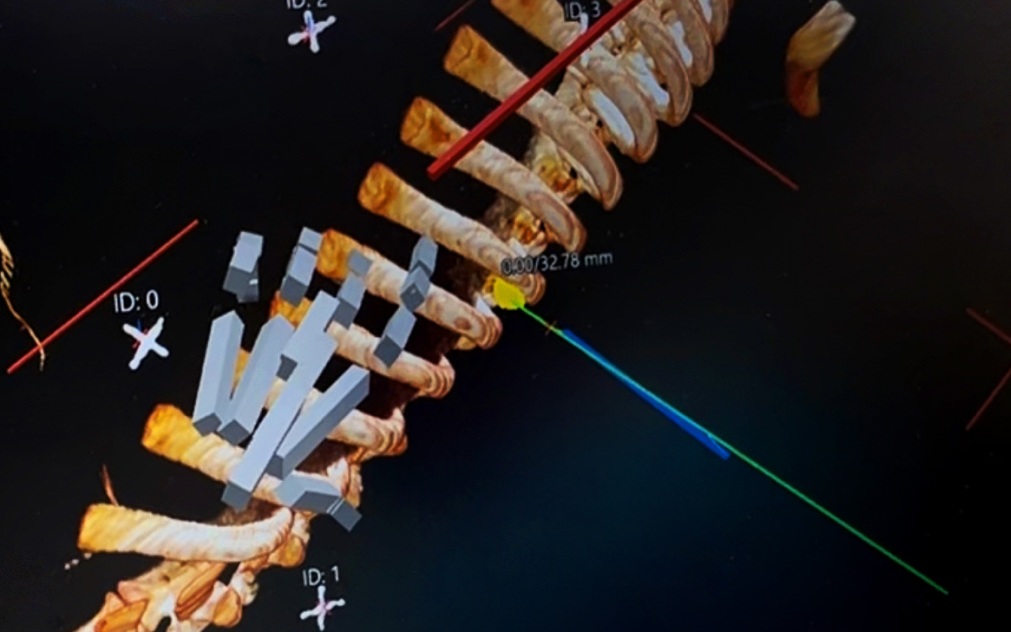
- Ability to obtain a 3D image of a selected area using the MedApp software based on a standard computed tomography (CT) image.
- Ability for the surgeon to insert a biopsy needle into a selected location with robotic assistance.
- Ability to insert the inPROBE® probe through the biopsy needle into a selected location and leave the probe in place for the required time.
Summary
The experiment combining the three technologies described above was conducted in response to the challenge raised by surgeons where during many biopsy procedures it is impossible to insert the biopsy needle into the small tumor for the first time, without the need to repeat the insertion and multiple scans of the patient by X-rays. The result of the experiment is considered a key contribution to the development of the inPROBE technology with robotic and visual support of the biopsy procedure. Based on the 3D image obtained based on a standard computed tomography (CT) image, the surgeon inserted the biopsy needle into the tumor, and then, for the purpose of molecular analysis, inserted the inPROBE® microsensor.
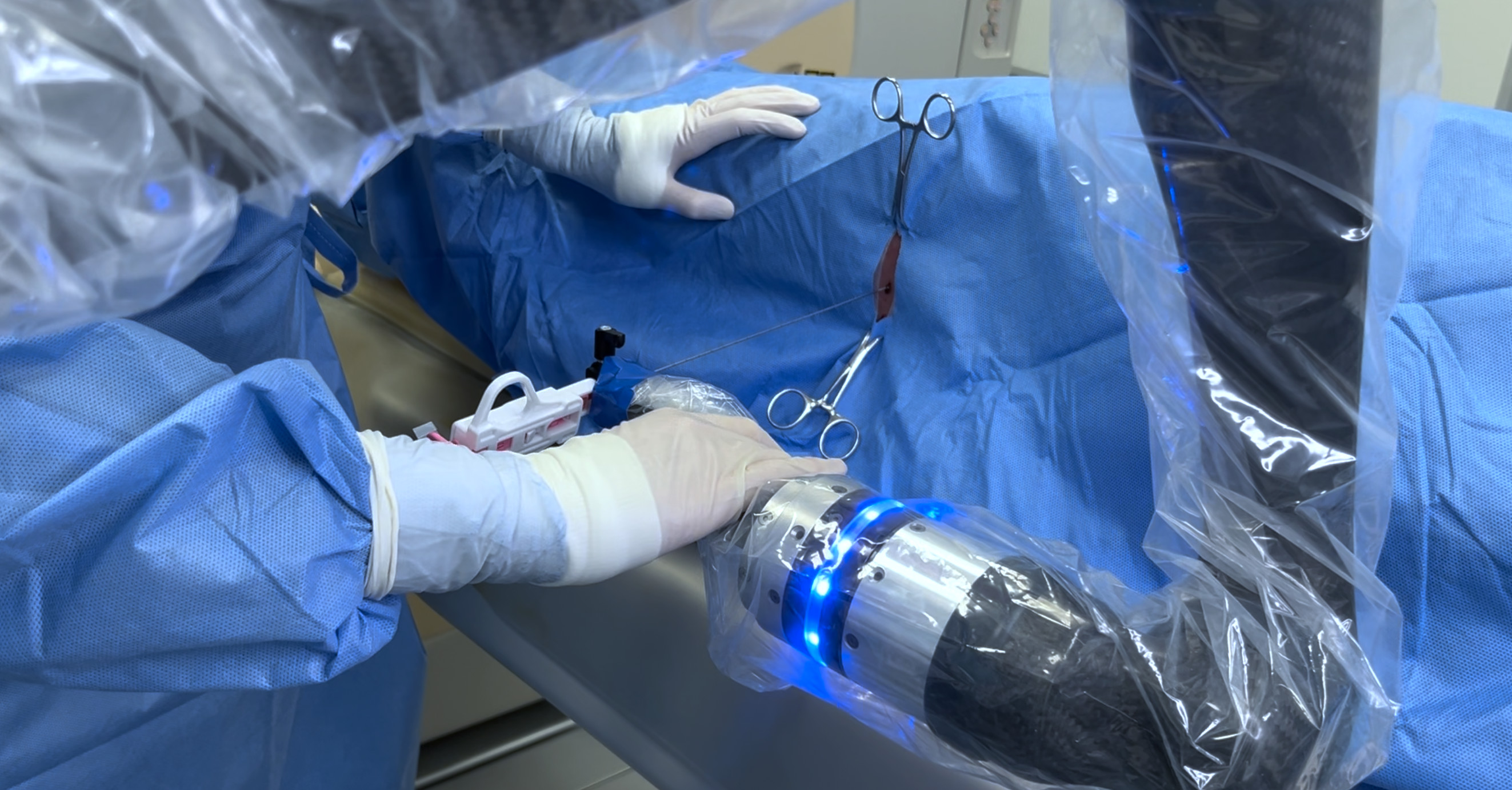
The biopsy needle insertion was performed both with robotic support and manually. During the experiment it was observed that the robotic support and 3D imaging give the surgeon the ability to insert the biopsy needle and then the inPROBE® probe into the small tumor already at the first insertion without the need for multiple X-ray radiation of the patient.
- The experiment was designed to demonstrate that the integration of the three analyzed technologies is feasible from a surgical perspective—and it was successful. As a result, a new medical product will be developed with a primary focus on the biopsy market. The average annual value of this market, considering only breast, lung, and liver tumors, is estimated to exceed EUR 4.5 billion. This estimate is based on the total number of biopsies reported in GLOBOCAN data and the cost of the extended inPROBE solution. The development of this new medical product has been identified as one of the key directions of SDS Optic’s technological advancement strategy. I would like to express my sincere gratitude to the employees and collaborators of SDS Optic, as well as to the team at the University of Life Sciences in Lublin, for their full commitment and invaluable contribution to the successful execution and outcome of this experiment. - says Marcin Staniszewski, CEO of SDS Optic S.A.
The Company announced the imminent publication of updates to the process of selected elements of the strategy and a video summary of the conducted experiment.
About SDS Optic S.A.
SDS Optic S.A. is an innovative biotechnology company developing a groundbreaking diagnostic technology that combines molecular biology, immunochemistry, medicine, and photonics.
The company's flagship solution is the inPROBE® platform — a micrometric fiber optic biosensor designed to enable future detection of cancer biomarkers, such as HER2, and other molecules in patient tissue.
The company has initiated studies on the application of inPROBE® technology during biopsies in breast cancer and in conjunction with endoscopic techniques in stomach cancer. Preliminary studies have confirmed the potential of the inPROBE® microsensor for HER2 biomarker detection in patients through both in-vivo and in-vitro procedures.
We Care About Your Privacy
SDS Optic S.A. uses cookies to improve and customize users experience on our website. By selecting 'Accept', you consent to the use of all cookies that gather and use information about your interactions with our site to provide personalized content and enhance your digital experience. Please read our Privacy Policy for more information.